- How Many Atoms Are In Iodine
- Atomic No Of Iodine Powder
- Atomic No Of Iodine
- Atomic No Of Iodine Group
- Atomic No Of Iodine Made
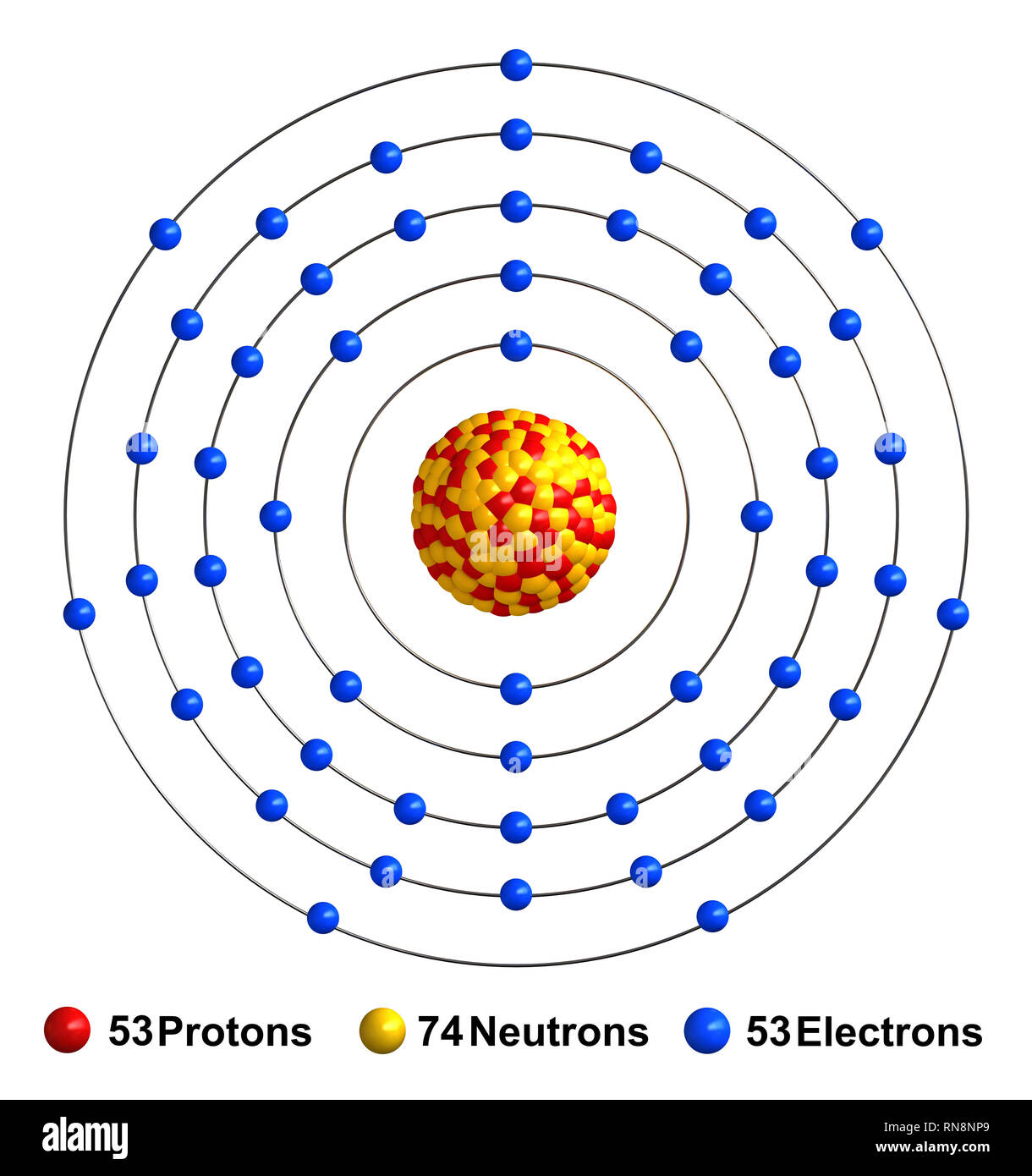
Atomic Number of Iodine. Atomic Number of Iodine is 53. Chemical symbol for Iodine is I. Number of protons in Iodine is 53. Atomic weight of Iodine is 126.90447 u or g/mol. Melting point of Iodine is 113,5 °C and its the boiling point is 184,4 °C. Iodine I-131 is a radioactive isotope of iodine with an atomic mass of 131, a half life of eight days, and potential antineoplastic activity. Selectively accumulating in the thyroid gland, iodine I 131 emits beta and gamma particles, thereby killing thyroid cells and decreasing thyroid hormone production. Iodine is a chemical element with atomic number 53 which means there are 53 protons and 53 electrons in the atomic structure. The chemical symbol for Iodine is I. Iodine is the heaviest of the stable halogens, it exists as a lustrous, purple-black metallic solid at standard conditions that sublimes readily to form a violet gas.
- Formula: I
- Molecular weight: 126.90447
- IUPAC Standard InChI:
- InChI=1S/I
- Download the identifier in a file.
- IUPAC Standard InChIKey:ZCYVEMRRCGMTRW-UHFFFAOYSA-N
- CAS Registry Number: 14362-44-8
- Chemical structure:
This structure is also available as a 2d Mol file - Permanent link for this species. Use this link for bookmarking this speciesfor future reference.
- Information on this page:
- Other data available:
- Data at other public NIST sites:
- Options:
Data at NIST subscription sites:
NIST subscription sites provide data under theNIST Standard ReferenceData Program, but require an annual fee to access.The purpose of the fee is to recover costs associatedwith the development of data collections included insuch sites. Your institution may already be a subscriber.Follow the links above to find out more about the datain these sites and their terms of usage.
Gas phase ion energetics data
Go To:Top, References, Notes Adobe photoshop elements trial download mac.
Data compilation copyrightby the U.S. Secretary of Commerce on behalf of the U.S.A.All rights reserved.
How Many Atoms Are In Iodine
Data evaluated as indicated in comments:
HL - Edward P. Hunter and Sharon G. Lias
L - Sharon G. Lias
Data compiled as indicated in comments:
B - John E. Bartmess
LL - Sharon G. Lias and Joel F. Liebman
LBLHLM - Sharon G. Lias, John E. Bartmess, Joel F. Liebman, John L. Holmes, Rhoda D. Levin, and W. Gary Mallard
LLK - Sharon G. Lias, Rhoda D. Levin, and Sherif A. Kafafi
RDSH - Henry M. Rosenstock, Keith Draxl, Bruce W. Steiner, and John T. Herron
| Quantity | Value | Units | Method | Reference | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IE (evaluated) | 10.45126 | eV | N/A | N/A | L |
| Quantity | Value | Units | Method | Reference | Comment |
| Proton affinity (review) | 608.2 | kJ/mol | N/A | Hunter and Lias, 1998 | HL |
| Quantity | Value | Units | Method | Reference | Comment |
| Gas basicity | 583.5 | kJ/mol | N/A | Hunter and Lias, 1998 | HL |
Electron affinity determinations
| EA (eV) | Method | Reference | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3.05900 ± 0.00010 | N/A | Pelaez, Blondel, et al., 2009 | Given: 3.0590463(38) eV; B |
| 3.059036 ± 0.000044 | LPD | Hanstorp and Gustafsson, 1992 | Given: 3.059038±0.000010 eV; B |
| 3.05917 ± 0.00039 | LOG | Webster, McDermid, et al., 1983 | B |
| 3.0620 ± 0.0020 | N/A | Neiger, 1975 | B |
| 3.060 ± 0.040 | N/A | Piani, Becucci, et al., 2008 | Stated electron affinity is the Vertical Detachment Energy; B |
| 3.0630 ± 0.0030 | N/A | Berry and Reimann, 1963 | B |
| 3.34476 | N/A | Check, Faust, et al., 2001 | Fe(CO)2-(q); ; ΔS(EA)=5.0; B |
Ionization energy determinations
| IE (eV) | Method | Reference | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10.45126 | EVAL | Lide, 1992 | LL |
| 10.43 ± 0.05 | PI | Grade and Rosinger, 1985 | LBLHLM |
| 10.4 ± 0.1 | EI | Hoareau, Cabaud, et al., 1981 | LLK |
| 10.5 | EI | Pittermann and Weil, 1980 | LLK |
| 10.45 | PE | Imre and Koenig, 1980 | LLK |
| 10.43 ± 0.02 | PE | De Leeuw, Mooyman, et al., 1978 | LLK |
| 10.451 | S | Moore, 1970 | RDSH |
| 10.45126 | S | Minnhagen, 1962 | RDSH |
Anion protonation reactions
+ =

By formula: I- + H+ = HI

| Quantity | Value | Units | Method | Reference | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ΔrH° | 1315.24 ± 0.084 | kJ/mol | D-EA | Pelaez, Blondel, et al., 2009 | gas phase; Given: 3.0590463(38) eV; B |
| ΔrH° | 1312.1 | kJ/mol | N/A | Check, Faust, et al., 2001 | gas phase; Fe(CO)2-(q); ; ΔS(EA)=5.0; B |
| Quantity | Value | Units | Method | Reference | Comment |
| ΔrG° | 1294.03 ± 0.25 | kJ/mol | H-TS | Pelaez, Blondel, et al., 2009 | gas phase; Given: 3.0590463(38) eV; B |
| ΔrG° | 1290.8 | kJ/mol | N/A | Check, Faust, et al., 2001 | gas phase; Fe(CO)2-(q); ; ΔS(EA)=5.0; B |

References
Go To:Top, Gas phase ion energetics data, Notes
Data compilation copyrightby the U.S. Secretary of Commerce on behalf of the U.S.A.All rights reserved.
Hunter and Lias, 1998
Hunter, E.P.; Lias, S.G.,Evaluated Gas Phase Basicities and Proton Affinities of Molecules: An Update,J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data, 1998, 27, 3, 413-656, https://doi.org/10.1063/1.556018. [all data]
Pelaez, Blondel, et al., 2009
Pelaez, R.J.; Blondel, C.; Delsart, C.; Drag, C.,Pulsed photodetachment microscopy and the electron affinity of iodine,J. Phys. B: Atom. Mol. Opt. Phys., 2009, 42, 12, 125001, https://doi.org/10.1088/0953-4075/42/12/125001. [all data]
Hanstorp and Gustafsson, 1992
Hanstorp, D.; Gustafsson, M.,Determination of the Electron Affinity of Iodine,J. Phys. B: Atom. Mol. Opt. Phys., 1992, 25, 8, 1773, https://doi.org/10.1088/0953-4075/25/8/012. [all data]
Webster, McDermid, et al., 1983
Webster, C.R.; McDermid, I.S.; Rettner, C.T.,Laser optogalvanic photodetachment spectroscopy: A new technique for studying photodetachment thresholds with application to I-,J. Chem. Phys. Can you download text messages from iphone to mac. , 1983, 78, 646. [all data]

Atomic No Of Iodine Powder
Neiger, 1975
Neiger, M.,Quantitative Investifgation of the Radiation of the Negative Iodine Ion,Z. Naturfor., 1975, 30, 474. [all data]
Piani, Becucci, et al., 2008
Piani, G.; Becucci, M.; Bowen, M.S.; Oakman, J.; Hu, Q.; Continetti, R.E.,Photodetachment and dissociation dynamics of microsolvated iodide clusters,Phys. Scripta, 2008, 78, 5, 058110, https://doi.org/10.1088/0031-8949/78/05/058110. [all data]
Berry and Reimann, 1963
Berry, R.S.; Reimann, C.W.,Absorption Spectrum of Gaseous Fluoride and the Electron Affinities of the Halogen Atoms,J. Chem. Phys., 1963, 38, 7, 1540, https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1776916. [all data]
Check, Faust, et al., 2001
Check, C.E.; Faust, T.O.; Bailey, J.M.; Wright, B.J.; Gilbert, T.M.; Sunderlin, L.S.,Addition of Polarization and Diffuse Functions to the LANL2DZ Basis Set for P-Block Elements,J. Phys. Chem. A,, 2001, 105, 34, 8111, https://doi.org/10.1021/jp011945l. [all data]
Lide, 1992
Lide, D.R. (Editor),Ionization potentials of atoms and atomic ionsin Handbook of Chem. and Phys., 1992, 10-211. [all data]
Grade and Rosinger, 1985
Grade, M.; Rosinger, W.,Correlation of electronic structures and stabilities of gaseous FeI2, Fe2I2 and Fe2I4 molecules, solid [FeI2], and iodine adsorbed on [Fe],Surf. Sci., 1985, 156, 920. [all data]
Hoareau, Cabaud, et al., 1981
Hoareau, A.; Cabaud, B.; Melinon, P.,Time-of-flight mass spectroscopy of supersonic beam of metallic vapours: Intensities and appearance potentials of Mx aggregates,Surf. Sci., 1981, 106, 195. [all data]
Pittermann and Weil, 1980
Pittermann, U.; Weil, K.G.,Massenspektrometrische Untersuchungen an Silberhalogeniden V: Verdampfung von Silberiodid,Ber. Bunsen-Ges. Phys. Chem., 1980, 84, 542. [all data]
Imre and Koenig, 1980
Imre, D.; Koenig, T.,The He(I) photoelectron spectrum of atomic iodine by photodissociation of molecular iodine,Chem. Phys. Lett., 1980, 73, 62. [all data]
Atomic No Of Iodine
De Leeuw, Mooyman, et al., 1978
De Leeuw, D.M.; Mooyman, R.; De Lange, C.A.,He(I) photoelectron spectroscopy of halogen atoms,Chem. Phys. Lett., 1978, 54, 231. [all data]
Atomic No Of Iodine Group
Moore, 1970
Moore, C.E.,Ionization potentials and ionization limits derived from the analyses of optical spectra,Natl. Stand. Ref. Data Ser., (U.S. Natl. Bur. Stand.), 1970, 34, 1. [all data]
Minnhagen, 1962
Minnhagen, L.,The energy levels of neutral atomic iodine,Ark. Hotel hideaway download mac. Fys., 1962, 21, 415. [all data]
Notes
Go To:Top, Gas phase ion energetics data, References
Atomic No Of Iodine Made
- Symbols used in this document:
EA Electron affinity IE (evaluated) Recommended ionization energy ΔrG° Free energy of reaction at standard conditions ΔrH° Enthalpy of reaction at standard conditions - Data from NIST Standard Reference Database 69:NIST Chemistry WebBook
- The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST)uses its best efforts to deliver a high quality copy of theDatabase and to verify that the data contained therein havebeen selected on the basis of sound scientific judgment.However, NIST makes no warranties to that effect, and NISTshall not be liable for any damage that may result fromerrors or omissions in the Database.
- Customer supportfor NIST Standard Reference Data products.
